<=Back
Viewed: 675 times
Share in:



<=KNEC Craft Certificate in ICT module 1 Basic Electronics past paper: July 2018 with video(s)
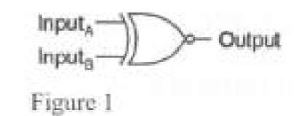
Figure 1 represents a logic gate. Draw the truth table of the logic gate.
Viewed: 675 times
Share in:



Questions List:
1. Outline four acceptors elements that would form a p-type region when a semiconductor is doped.
2. Draw a closed circuit of three inductors (L1,L2 and L3) in series, showing the current (I) flow and voltage (V1,V2 and V3) across each inductor.
3. Determine the arithmetic operation #345_8 + 43F_16# leaving the answer in decimal equivalent.
4. Explain two characteristics of a Static Random Access Memory
5. Modern computers use ROM in the manufacture of their memories. Explain two primarily uses of ROM
6. Explain two application areas of gray code in computers.
7. Computer designers prefers using hexadecimal number system. State two reasons for this.
8. Define each of the following terms as used in electrical circuits. i)Overcurrent ii)Wattage
9. Calculate each of the following octal arithmetic i)234 – 137 ii)654 + 216
10. With the aid of a sketch, implement an AND gate with two inputs using NAND logic gates
11. Determine the excess-3 equivalent of each of the following decimal numbers i)147 ii)2543
12. Outline four examples of the read only memory
13. The rapid development of electronic components has changed the face the electronic world. Explain two emerging trends of such electronic components in the society.
14. Using BCD evaluate 91 + 79
15. Differentiate between power and energy as used in electrical circuits.
16. Explain two primary bonds that could be found in a semiconductor
17. Differentiate between electrical conductivity and electrical resistivity as used in DC circuits.
18. Figure 1 represents a logic gate. Draw the truth table of the logic gate.
19. Figure 2 represents a closed circuit. Use it to answer the following questions. I)Determine the total resistance in the circuit given that R1 = 10 Ὠ , R2 =60Ὠ , R3 = 50Ὠ and R4 = 40Ὠ II)Describe the flow of the current in the current in the resistors R3 and R4
20. Table 1 represent a truth table for a logic circuit. Use it to answer the questions that follow. i)Derive the boolean expression for the sum of products ii)Use K-map to simplify the boolean expression
21. Explain three circumstances under which two’s complement is required in computer use.
22. Distinguish between electrode and electrolyte
23. Define impedance as used in electronics
24. Convert the following decimal equivalent to their BCD numbers. I) 598 II) 96.72
25. Evaluate the binary arithmetic #D_16times3_8# to its octal equivalent.
26. Simplify the boolean function using boolean algebra laws.
27. Outline three disadvantages of integrated circuits.
28. Draw a closed circuit with two batteries and three resistors (R1,R2 and R3) in parallel showing the flow of current.
29. Figure 3 represents an atom structure of an element X. identify the part labelled I,II,III,IV
30. Explain each of the following terms as applied in batteries I) Float charging II) Memory effect
1. Outline four acceptors elements that would form a p-type region when a semiconductor is doped.
2. Draw a closed circuit of three inductors (L1,L2 and L3) in series, showing the current (I) flow and voltage (V1,V2 and V3) across each inductor.
3. Determine the arithmetic operation #345_8 + 43F_16# leaving the answer in decimal equivalent.
4. Explain two characteristics of a Static Random Access Memory
5. Modern computers use ROM in the manufacture of their memories. Explain two primarily uses of ROM
6. Explain two application areas of gray code in computers.
7. Computer designers prefers using hexadecimal number system. State two reasons for this.
8. Define each of the following terms as used in electrical circuits. i)Overcurrent ii)Wattage
9. Calculate each of the following octal arithmetic i)234 – 137 ii)654 + 216
10. With the aid of a sketch, implement an AND gate with two inputs using NAND logic gates
11. Determine the excess-3 equivalent of each of the following decimal numbers i)147 ii)2543
12. Outline four examples of the read only memory
13. The rapid development of electronic components has changed the face the electronic world. Explain two emerging trends of such electronic components in the society.
14. Using BCD evaluate 91 + 79
15. Differentiate between power and energy as used in electrical circuits.
16. Explain two primary bonds that could be found in a semiconductor
17. Differentiate between electrical conductivity and electrical resistivity as used in DC circuits.
18. Figure 1 represents a logic gate. Draw the truth table of the logic gate.
19. Figure 2 represents a closed circuit. Use it to answer the following questions. I)Determine the total resistance in the circuit given that R1 = 10 Ὠ , R2 =60Ὠ , R3 = 50Ὠ and R4 = 40Ὠ II)Describe the flow of the current in the current in the resistors R3 and R4
20. Table 1 represent a truth table for a logic circuit. Use it to answer the questions that follow. i)Derive the boolean expression for the sum of products ii)Use K-map to simplify the boolean expression
21. Explain three circumstances under which two’s complement is required in computer use.
22. Distinguish between electrode and electrolyte
23. Define impedance as used in electronics
24. Convert the following decimal equivalent to their BCD numbers. I) 598 II) 96.72
25. Evaluate the binary arithmetic #D_16times3_8# to its octal equivalent.
26. Simplify the boolean function using boolean algebra laws.
27. Outline three disadvantages of integrated circuits.
28. Draw a closed circuit with two batteries and three resistors (R1,R2 and R3) in parallel showing the flow of current.
29. Figure 3 represents an atom structure of an element X. identify the part labelled I,II,III,IV
30. Explain each of the following terms as applied in batteries I) Float charging II) Memory effect